At their foundation, AI systems are massive data engines. Training, deploying, and operating AI models requires handling enormous datasets—and the speed at which data moves between storage and compute can make or break performance. In many organizations, this data movement becomes the biggest constraint. Even with better algorithms, companies frequently point to limitations in data infrastructure as the top barrier to AI success.
During the recent AI Infrastructure Field Day, Solidigm—a maker of high-performance SSDs built for AI workloads—shared how data travels through an AI training workflow and why storage plays an equally important role as compute. Their central point: AI training succeeds when storage and memory work in sync, keeping GPUs fully fed with data. Since high-bandwidth memory (HBM) can’t store entire datasets, orchestrating the flow between storage and memory is essential.
The takeaway: Well-designed storage architecture ensures GPUs can run at peak capacity, provided data arrives quickly and efficiently.
Raw Data → Data Preparation
Raw Data Set
The process begins with large volumes of unstructured data written to disk, usually on network-attached storage (NAS) systems optimized for density and energy efficiency.

Data Prep 1
Batches of raw data are pulled into compute server memory, where the CPU performs ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) to clean and normalize the information.
Data Prep 2
The cleaned dataset is then stored back on disk and also streamed to the machine learning algorithm running on GPUs.
Training → Archiving
Training
From a data perspective, training generates two outputs:
- The completed model, written first to memory and then saved to disk.
- Multiple “checkpoints” saved during training to enable recovery from failures—these are often written directly to disk.
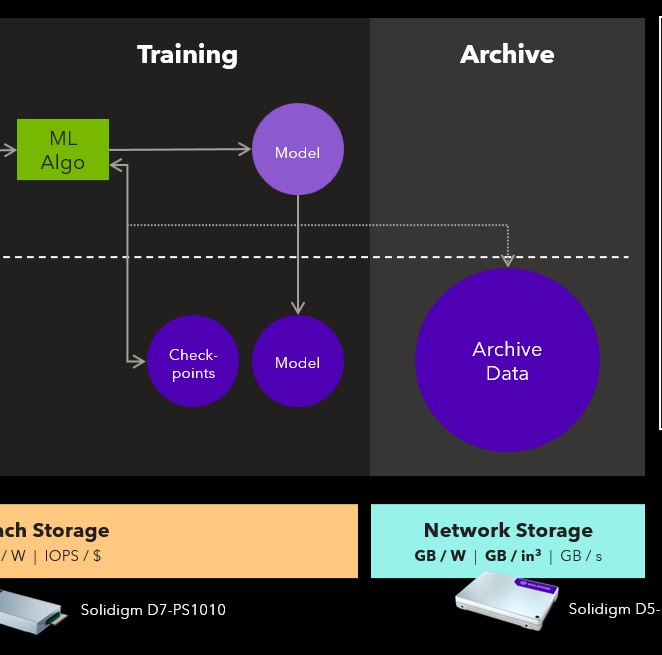
Archive
Once training is complete, key datasets and outputs are archived in network storage for long-term retention, audits, or reuse.
NVIDIA GPUDirect Storage
A noteworthy technology in this process is NVIDIA GPUDirect Storage, which establishes a direct transfer path from SSDs to GPU memory. This bypasses the CPU and system memory, reducing latency and improving throughput.

Final Thought
While having more data can lead to better model accuracy, efficiently managing that data is just as important. Storage architecture decisions directly impact both performance and power usage—making them a critical part of any serious AI strategy.
Extra-credit reading:
Pau for now…



 Posted by Barton George
Posted by Barton George